Ransomware In Q3 2020: Recapping Check Point Research Findings
Organizations around the world are at the forefront of a massive wave of ransomware attacks. In the last three months alone, the average daily number of ransomware attacks has increased by 50%. As the frequency and intensity of these attacks continue to grow, their impact on businesses grows exponentially.
Claiming a new victim every ten seconds, ransomware has proved to be a lucrative attack method for cybercriminals. Check Point Research studied and analyzed this wave of recent attacks. This article details characteristics, the targeted countries, potential reasons for the trend, and tips on how organizations can prevent ransomware attacks.
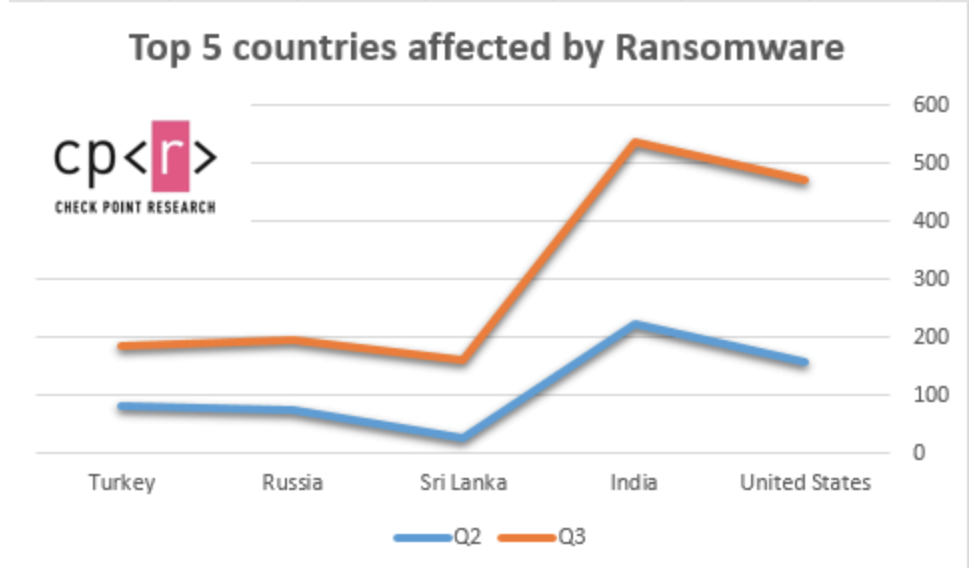
Top Countries Affected by Ransomware in Q3 2020
Over the past three months, the average daily number of attacks has increased by 50% compared to the first half of 2020. The number of ransomware attacks in the United States has doubled (by about 98%) in the past three months, making it the number 1 country.
Top 5 countries affected by ransomware in Q3 by the number of attacks:
- USA (up 98.1%);
- India (up 39.2%);
- Sri Lanka (up 436%);
- Russia (up 57.9%);
- Turkey (up 32.5%)
Why is this happening now?
The current pandemic is forcing organizations to make quick changes to their business structures, often leaving gaps in their IT systems. These flaws have given cybercriminals the ability to exploit security flaws and infiltrate an organization’s network. Hackers encrypt hundreds of thousands of files, incapacitating users, and often taking entire networks hostage. In some cases, organizations simply choose to pay the price instead of dealing with encrypted files and rebuilding their IT systems. This creates a vicious circle – the more “success” of this type of attack, the more often they occur.
Cybercriminals have also begun to implement a new tactic in their ransomware programs: double extortion. In what has become a trend since Q1 2020, attackers are adding an extra stage to their attacks. Before encrypting the victim’s databases, attackers extract large amounts of confidential information and threaten to publish this information if their ransom demands are not paid.
Driven by fear, organizations sometimes choose to pay ransomware immediately to avoid revealing their valuable data. Recently, various ransomware operators have taken advantage of the current pandemic and used this tactic to force hospitals and medical research institutes to pay a ransom, putting patients’ lives at risk.
In addition, after a 5-month hiatus, Emotet has again ranked as # 1 most wanted malware, affecting 5% of organizations worldwide. Emotet is an advanced self-propagating modular Trojan. It was originally a banking Trojan, but has recently been used as a distributor of other malware or malware campaigns.
Emotet operations sell information about their infected victims to ransomware distributors, and since they are already infected, these victims are vulnerable to new attacks. This makes ransomware attacks even more “effective” for an attacker since more infected targets mean more entry points for ransomware attacks.
Ryuk ransomware in focus
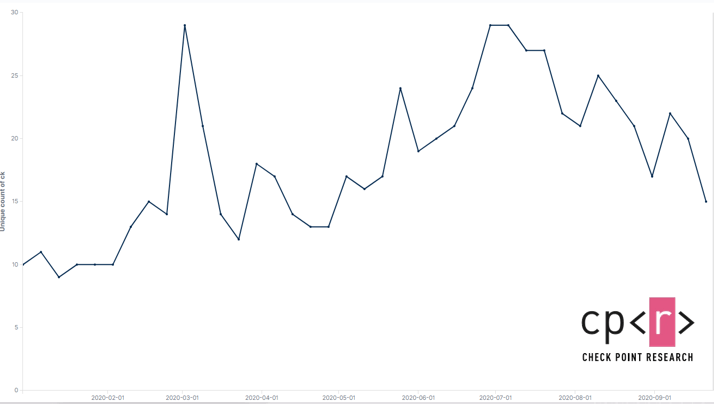
Unlike conventional ransomware, which is systematically spread through massive spam campaigns and exploit kits, Ryuk is used exclusively for specialized targeted attacks. Ryuk was first discovered in mid-2018, and shortly after that, Check Point Research published its first thorough analysis of ransomware that was then targeting the United States. Ryuk’s activity has increased significantly since July 2020, attacking about 20 organizations per week.
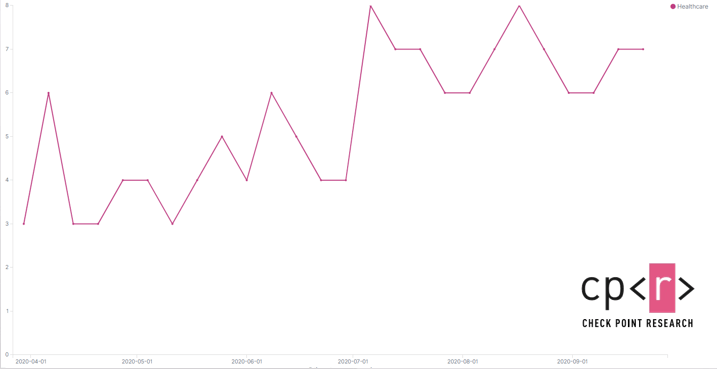
The number of healthcare organizations targeted by Ryuk is growing steadily, and the percentage of healthcare organizations affected by ransomware has nearly doubled, from 2.3% in the second quarter to 4% in the third quarter. In addition, healthcare is the number one industry in the United States.
Our data comes from ThreatCloud, Check Point’s threat intelligence engine that comes from hundreds of millions of sensors around the world, enriched with AI-powered engines and exclusive research data from Check Point Research.
Ransomware Prevention
So what can organizations do to reduce the risk of ransomware attacks? Here are some tips to consider.
General good practice
Education
Educating users on how to identify and avoid potential ransomware attacks is critical. Many of the current cyberattacks start with a targeted email that doesn’t even contain malware but is a socially engineered message that prompts a user to click a malicious link. User training is often considered one of the most important defenses an organization can deploy.
Continuous data backup. Backing up your data regularly as a routine process is a very important practice to prevent data loss and to be able to recover it in the event of damage or malfunction of disk equipment.
Functional backups can also help organizations recover from ransomware attacks.
Patching
Patching is an important part of protecting against ransomware attacks, as cybercriminals often look for the latest exploits found in the available patches and then select systems that have not yet been patched. It is critical that organizations ensure that all systems are updated with the latest patches as this reduces the number of potential business vulnerabilities that an attacker could exploit.
Best security practices
Endpoint Protection
Regular signature-based antivirus is a highly effective solution to prevent known attacks and should be implemented in any organization as it protects against most malware attacks faced by an organization.
Network Protection
Advanced corporate network defenses such as IPS, Network Antivirus, and Anti-Bot are also critical and effective in preventing known attacks.
Advanced technologies such as sandboxing can analyze new, unknown malware, execute it in real-time, look for signs that it is malicious code, and as a result, block it and prevent endpoint infection and spread elsewhere in the organization.
Stay tuned with Software Focus!

